 Ultimate Guide to Ball Valve Selection: Floating vs. Trunnion vs. Multi-Port Designs 2
Ultimate Guide to Ball Valve Selection: Floating vs. Trunnion vs. Multi-Port Designs 2
Selecting the right ball valve for industrial systems requires careful consideration of application needs and valve design. Raymon Valve Co. Ltd. stands out as a trusted manufacturer, known for high temperature and high pressure ball valves. Industries rely on ball valves for critical operations.
- Oil and Gas uses ball valves in high-pressure environments.
- Water and Wastewater treatment drives demand for advanced valve solutions.
- Chemical Processing benefits from materials designed for durability.
Ball Valve Selection depends on matching each valve type to the demands of the specific industry and operating conditions.
Ball Valve Selection: Quick Guide
Ball valve selection plays a crucial role in industrial system performance. Choosing the right valve type depends on pressure, temperature, media compatibility, and operational needs. Raymon Valve Co. Ltd. offers expertise in high temperature and high pressure ball valves, ensuring reliable solutions for demanding environments.
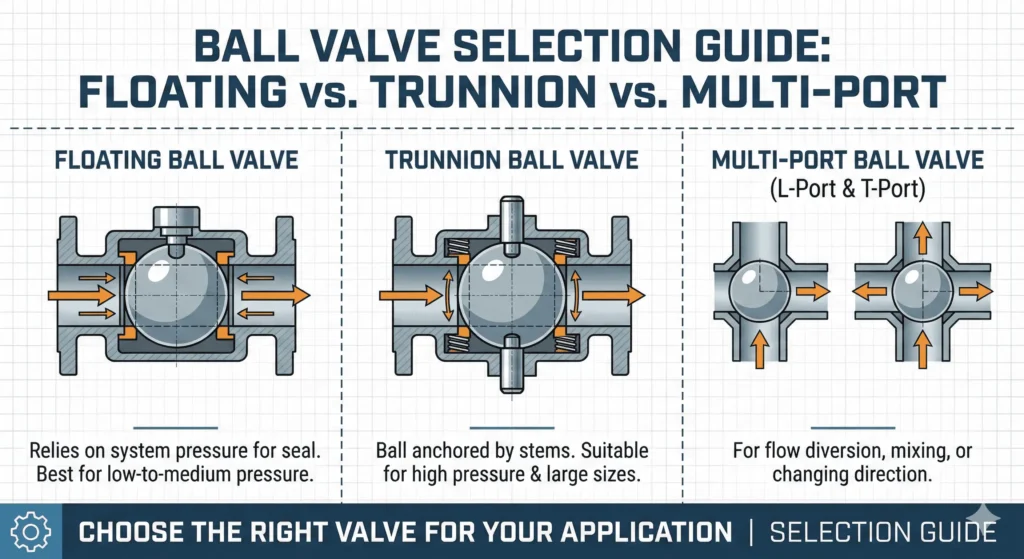
Choosing Floating Ball Valves
Best for low to medium pressure applications and compact installations.
Floating ball valves suit systems where pressure and temperature remain moderate. These valves rely on fluid pressure to create a tight seal. Maintenance is straightforward due to fewer moving parts. Operators often select floating ball valves for water treatment, chemical processing, and small-diameter pipelines.
Tip: Always check the valve’s pressure rating. For example, a floating ball valve rated at 150 psi handles pressures up to that limit safely.
Key advantages:
- Compact design fits tight spaces.
- Lower cost compared to other designs.
- Easier maintenance and part replacement.
| Criteria | Floating Ball Valve |
|---|
| Pressure Range | Low to medium |
| Torque Requirements | Higher |
| Size | More compact |
| Sealing Mechanism | Relies on fluid pressure |
| Maintenance | Easier |
| Cost | More affordable |
Choosing Trunnion Ball Valves
Ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature, and large-diameter pipelines.
Trunnion ball valves feature a fixed ball supported at both ends. This design withstands high fluid pressure and flow rates, reducing wear and tear. Multiple seals ensure a secure shut-off, minimizing leakage risk. Industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation prefer trunnion ball valves for critical processes.
Key advantages:
| Criteria | Trunnion Ball Valve |
|---|
| Pressure Range | Suitable for high-pressure |
| Torque Requirements | Lower |
| Size | Larger due to additional components |
| Sealing Mechanism | Seats move to seal ball |
| Maintenance | More complex |
| Cost | More expensive |
Note: Trunnion ball valves provide bidirectional sealing, making them suitable for large-diameter pipelines and high-pressure environments.
Choosing Multi-Port Ball Valves
Best for complex flow control and multi-directional piping systems.
Multi-port ball valves allow operators to direct flow between multiple channels. These valves simplify piping layouts and reduce the need for multiple valves. Facilities use multi-port ball valves in mixing, diverting, or distributing fluids across different process lines.
Key advantages:
- Streamlines system design by combining several flow paths.
- Reduces installation space and cost.
- Enhances automation and control capabilities.
Quick Ball Valve Selection Checklist:
- Confirm operating pressure and temperature requirements.
- Ensure media compatibility with valve materials.
- Assess flow control needs, including throttling or shut-off.
- Evaluate pipeline size and layout constraints.
- Determine automation and remote operation needs.
- Consider maintenance access and expected lifespan.
Ball valve selection depends on matching the valve type to the specific demands of the application. Raymon Valve Co. Ltd. provides expert guidance and high-quality ball valves for every industrial need. Operators should review the common types of ball valves and select the design that best fits their system requirements.
Types of Ball Valves
Ball valves come in several designs, each serving specific industrial needs. Understanding the main types of ball valves helps operators select the right solution for their systems. The three most common types of ball valves are floating ball valves, trunnion ball valves, and multi-port ball valves.
| Category | Description |
|---|
| Floating Ball Valve | The ball floats and is pressed against the sealing surface by medium pressure, suitable for medium and low pressure. |
| Trunnion Ball Valve | The ball is attached between two posts, allowing for reduced operating torque. |
| Multi-Port Ball Valve | Have multiple ports for diverting or mixing, reducing the need for additional piping. |
Floating Ball Valves Explained
Floating ball valves use a ball that is not fixed but floats between two seats. The pressure of the fluid pushes the ball against the downstream seat, creating a tight seal. These valves work best in low to medium pressure systems. Operators often choose floating ball valves for water, HVAC, and light industrial applications.
- Typical pressure ratings include ANSI 150#, 300#, and 600#.
- Common failure modes:
- Fail to close or open due to corrosion.
- Fail to regulate flow.
- External leakage from worn seals.
Tip: Floating ball valves are ideal for clean liquids and gases.
Trunnion Ball Valves Explained
Trunnion ball valves feature a ball supported by two shafts, or trunnions. This design reduces the force needed to operate the valve, even at high pressures. Trunnion ball valves handle abrasive or corrosive media better than floating designs. They are common in oil, gas, and petrochemical plants.
| Component | Material Options |
|---|
| Body Materials | Carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, specialty alloys |
| Sealing Materials | PTFE, RPTFE, PEEK, metal seals |
Trunnion ball valves offer robust sealing and long service life, especially in harsh environments.
Multi-Port Ball Valves Explained
Multi-port ball valves have three or more ports. These valves allow operators to control flow between multiple channels. Common flow configurations include:
- Shut off flow
- Switch flow between two sources
- Combine or split flow between destinations
- Divert flow from one source to another
Multi-port ball valves improve efficiency in batch processing by mixing, diverting, or distributing fluids through several outlets. The materials and construction of ball valves ensure durability and reliable performance in demanding applications.
Industrial Uses of Ball Valves
Ball valves play a vital role in many industries. They provide reliable shut-off and flow control in critical processes. Operators select these valves for their durability and ability to handle harsh conditions. Common ball valve applications include:
- Oil and gas plants use ball valves for high-pressure and high-temperature pipelines.
- Chemical processing facilities rely on them for corrosion resistance and safe handling of aggressive media.
- Power generation stations install ball valves in steam and cooling systems for robust performance.
- Water and wastewater treatment plants use them for efficient flow control and easy maintenance.
Many industries choose SMO 254 ball valves for their corrosion resistance. These valves maintain performance under extreme conditions and offer robust construction for long service life.
Performance Factors: Pressure, Temperature, Materials
Selecting the right ball valves depends on several key performance factors. Material selection, pressure ratings, and sealing technology all influence valve reliability. The following table highlights important considerations for high-pressure steam systems:
| Performance Factor | Description |
|---|
| Material Selection | Materials must withstand high temperatures and pressures for reliable operation. |
| Pressure Ratings | Valves need ratings that match the system’s maximum pressure. |
| Sealing Technologies | Advanced seals prevent leaks in high-temperature environments. |
| Safety Protocols | Safety measures protect against pressure spikes and thermal stress. |
The materials used in ball valves affect their temperature and pressure ratings. Metals like stainless steel lose strength at higher temperatures, which lowers the maximum pressure the valve can handle. For example, stainless steel grades 304 and 316 have continuous temperature limits up to 1,700°F (925°C). As temperature rises, the allowable working pressure decreases. Manufacturers consider the chemical composition and mechanical properties of materials, as well as the coefficient of thermal expansion, to ensure safe operation. ANSI and DIN standards provide guidelines for temperature and pressure relationships, helping operators select the right valve for each application.
Comparing Ball Valves
Operation and Maintenance
Ball valves serve as essential shutoff valves in industrial systems. Maintenance routines help ensure reliable operation and extend service life. Operators perform regular checks to prevent leaks and maintain smooth function. The following table outlines typical maintenance tasks and their recommended frequency for floating, trunnion, and multi-port ball valves:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|
| Visual inspection for leaks | Daily/Weekly |
| Stem packing leak checks | Daily/Weekly |
| Smooth operation of actuators | Daily/Weekly |
| Position indicator verification | Daily/Weekly |
| Exterior cleaning | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Flange bolt torque checks | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Lubrication according to valve specs | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Seat leakage tests | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Full valve disassembly and inspection | Annual |
| Surface cleaning and lapping | Annual |
| Hydrostatic and seat tightness testing | Annual |
Operators find that trunnion ball valves require less frequent major maintenance due to their robust design. Floating ball valves may need more attention in high-pressure systems. Multi-port ball valves simplify piping layouts, but regular inspection remains important for all types.
Main answer: Trunnion ball valves generally offer longer service life and reduced wear, making them ideal for continuous operation in demanding environments.
Cost and Suitability
Cost plays a key role in selecting stop valves for industrial applications. Initial investment and long-term value differ among ball valve types. The table below compares average costs and expected value:
| Valve Type | Initial Cost | Long-Term Value |
|---|
| Floating Ball Valve | Lower | May need more frequent replacements |
| Trunnion Ball Valve | Higher | Greater durability and longer service life |
Floating ball valves offer a cost-effective solution for manual ball valve installations in low-pressure systems. Trunnion ball valves provide greater durability, making them suitable for electric ball valve automation and high-pressure pipelines. Multi-port ball valves reduce installation costs by combining several flow paths, which can lower total system expenses.
Main answer: Trunnion ball valves deliver higher long-term value due to their durability and extended service life, especially in harsh environments.
Performance Comparison of Fixed Ball Valves and Floating Ball Valves
Fixed ball valves, also known as trunnion ball valves, use a ball supported by trunnions at both ends. This design creates a reliable sealing mechanism and requires low operating torque. Floating ball valves rely on fluid pressure to press the ball against the seat, which can increase wear over time.
- Fixed ball valves comply with API 6D standards for shut-off valve performance in high-pressure pipelines.
- The trunnion design supports a 25-year design life, often with maintenance-free operation.
- Operators benefit from lower total cost of ownership (TCO) due to reduced maintenance and fewer replacements.
Main answer: Fixed ball valves provide superior sealing, lower operating torque, and longer service life, making them the preferred choice for critical isolation valves in high-pressure applications.
Selecting the Right Ball Valves: Step-by-Step
Define Application Needs
Selecting the right ball valves starts with a clear understanding of the application. Operators in industries like petrochemical, power generation, and water treatment must identify the specific requirements of their systems. The following points help define these needs:
- Media type: Gases, liquids, or slurries each present unique challenges. Corrosive or abrasive media may require special materials or coatings.
- Pressure and temperature: High-pressure or high-temperature systems often need trunnion-mounted or pneumatic ball valve designs.
- Material compatibility: The selected material must resist corrosion and erosion. Stainless steel works well for aggressive chemicals, while plastic suits less demanding applications.
Main answer: Operators must match the ball valve design to the system’s media, pressure, and temperature to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Raymon Valve Co. Ltd. offers expert support to help define these needs, ensuring each solution fits the application.
Material and Sizing Considerations
Material selection and sizing are key features to consider when selecting the right ball valves. The wrong choice can lead to leaks, corrosion, or even system failure. Operators should focus on:
- Chemical compatibility: The valve material must withstand the chemicals in the process.
- Operating temperature: Materials must handle the highest expected temperature.
- Pressure requirements: The valve must safely contain the system’s maximum pressure.
- Flow characteristics: The size and shape of the valve affect flow rates and control.
Common materials include stainless steel, super duplex steels, exotic alloys, and specialized coatings. For corrosive environments, these materials provide the best protection. Sizing the valve correctly ensures efficient flow and prevents pressure drops.
Main answer: Proper material and sizing choices extend valve life and maintain system performance.
Raymon Valve’s engineers help select the right materials and sizes, offering customization for unique requirements. OEM and ODM services allow for specialized solutions, including options like true union ends, double o-ring stem seals, and integrated mounting pad features.
Connection Types and Standards
Connection types and standards play a major role in installation and maintenance. The right connection ensures a secure fit and reliable operation. The table below compares common connection types:
| Connection Type | Advantages |
|---|
| Socket Weld Ball Valve | Strong, reliable, easy to weld and install, ideal for high-pressure use. |
| Butt Weld Ball Valve | Smooth flow, durable welded joint, best for high-purity applications. |
| Tri-Clamp Ball Valve | Hygienic, easy cleaning, quick disassembly, great for sanitary systems. |
| Wafer Ball Valve | Compact, economical, simple installation, suitable for low-pressure use. |
Different connection types affect installation ease and maintenance. Flanged connections are simple to install and maintain but need more space. Threaded connections are cost-effective and easy to use for smaller sizes and lower pressures.
The table below lists widely recognized standards for ball valves:
| Standard | Description |
|---|
| ANSI | U.S. guidelines for design, materials, and performance (e.g., ANSI B16.34). |
| ISO | International standards for design, construction, and testing (e.g., ISO 17292). |
| API | Oil and gas industry standards, including pipeline valves (e.g., API 6D). |
Main answer: Choosing the right connection type and standard ensures compatibility, safety, and ease of maintenance.
Raymon Valve provides integrated mounting pad and integrated support bracketing options for easier installation and automation.
Maintenance and Longevity
Maintenance is one of the key features to consider for long-term performance. Regular care extends the operational life of ball valves and reduces the risk of failure. The following steps help maintain valve reliability:
- Schedule regular inspections to check for leaks or wear.
- Lubricate moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
- Replace seals and gaskets as needed, especially in high-use systems.
- Plan preventive maintenance during non-critical periods to avoid shutdowns.
Well-maintained valves operate more efficiently and predictably. They help prevent dangerous situations, such as sudden pressure releases or leaks. Preventive maintenance costs less than emergency repairs or early replacements.
Main answer: Regular maintenance significantly increases the lifespan and reliability of ball valves, especially in complex systems like multi-port or pneumatic ball valve installations.
Raymon Valve supports customers with after-sales service and maintenance guidance. Customization options, such as integrated mounting pad and double o-ring stem seals, further enhance durability and ease of service.
Tip: Avoid common mistakes in ball valve selection by consulting with experts and following a maintenance schedule.
Selecting the right ball valves involves careful analysis of application needs, materials, sizing, connection types, and maintenance. Raymon Valve Co. Ltd. offers expert guidance, customization, and OEM/ODM services to ensure every solution meets the highest standards.
Floating, trunnion, and multi-port ball valves each serve unique roles in industrial systems. Floating designs work best for moderate pressure, trunnion types excel in high-pressure pipelines, and multi-port valves simplify complex flow control. Matching the valve type to system requirements ensures safe and efficient operation. Operators should review the checklist below before final selection.
| Checklist Item | Description |
|---|
| Temperature and Pressure Ratings | Ensure the valve can withstand the service fluid’s temperature and pressure. |
| Estimated Annual Cycles | Assess how often the valve will operate. |
| Intended Use | Identify the specific application. |
| Materials | Verify compatibility and corrosion resistance. |
| Certifications | Confirm industry health and safety standards. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Plan for inspection and upkeep. |
For complex or high-pressure applications, consulting Raymon Valve Co. Ltd. helps operators achieve reliable solutions.
FAQ
What is a full port ball valve and why is it important?
A full port ball valve features an internal diameter equal to the pipeline. This design allows unrestricted flow, reducing pressure drop. Operators select full port valves for applications needing maximum flow capacity and minimal turbulence. Full port valves support efficient system performance and easy cleaning.
How does a full port ball valve ensure unrestricted flow?
Full port ball valves have a bore size matching the pipe. This design eliminates bottlenecks. The result is unrestricted flow, which prevents clogging and supports high flow rates. Full port valves work well in systems where unrestricted flow is critical for process efficiency.
When should operators choose a full port ball valve over a standard port?
Operators choose full port ball valves for processes needing unrestricted flow. These valves suit applications with slurries, viscous fluids, or frequent cleaning. Full port valves also help when pressure drop must stay low. Standard port valves fit less demanding systems.
Can full port ball valves handle high-pressure applications?
Full port ball valves can handle high-pressure systems when built with proper materials. Many industries use full port valves in high-pressure pipelines. The design supports unrestricted flow, even under demanding conditions. Always check the valve’s pressure rating before installation.
What are the main benefits of using full port ball valves in industrial systems?
Full port ball valves offer unrestricted flow, easy maintenance, and reduced pressure loss. Operators benefit from simple cleaning, minimal clogging, and reliable shut-off. Full port valves improve efficiency in pipelines that require high flow rates and frequent operation.